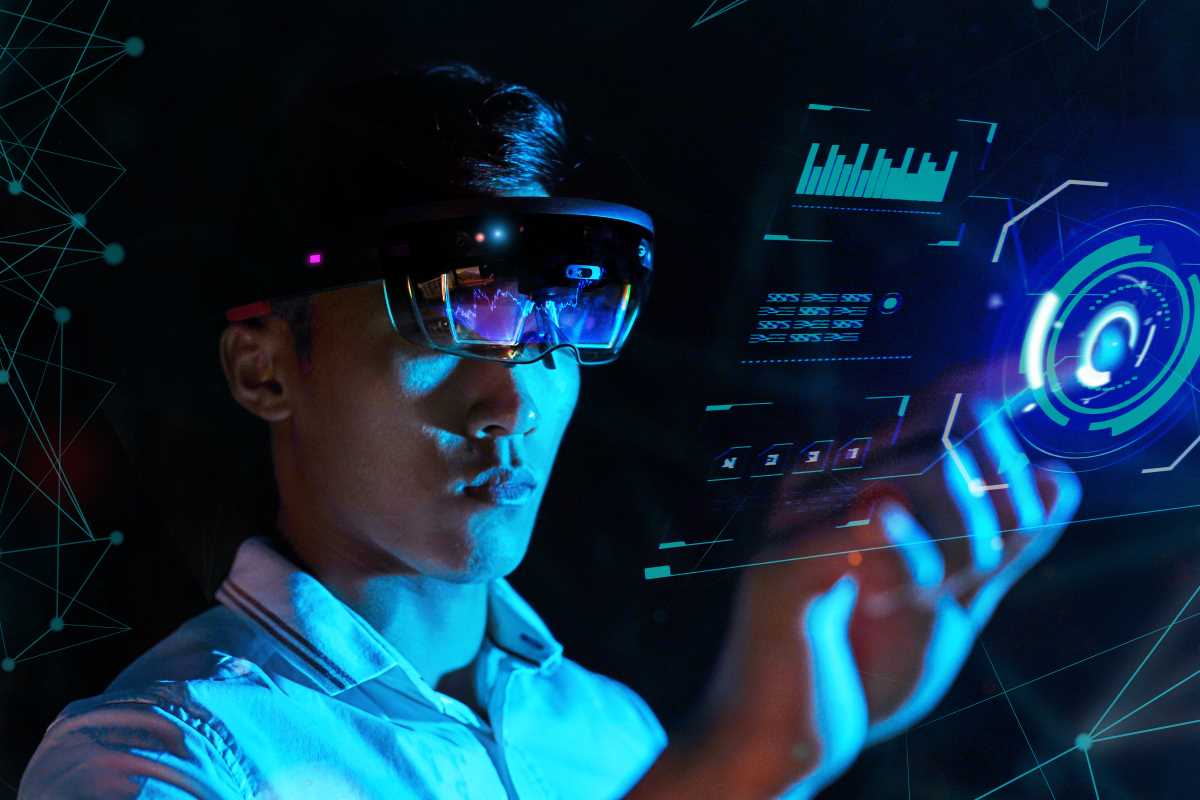
Augmented Reality (AR) is transforming how people interact with digital content and the physical world by overlaying virtual elements onto real environments. AR is poised to become a central force in creating immersive experiences that blur the lines between the virtual and real worlds, from gaming and entertainment to education and healthcare. As the technology advances, its potential to redefine industries, enhance user engagement, and reshape daily life becomes increasingly evident. This article explores the future of AR and how it will revolutionize the concept of immersive experiences.
Advancements in AR Technology
Improvements in hardware, software, and connectivity drive the evolution of AR technology. Modern AR experiences are becoming more realistic, responsive, and accessible, thanks to the following developments:
- Enhanced Hardware: AR-enabled devices such as smart glasses, headsets, and even smartphones are becoming more lightweight, powerful, and user-friendly. Companies like Apple, Meta, and Microsoft are investing heavily in hardware advancements, aiming to deliver seamless AR experiences. For instance, AR glasses now feature high-resolution displays, advanced sensors, and long-lasting batteries that make extended use possible.
- AI Integration: Artificial intelligence plays a vital role in improving AR. AI enhances object recognition, spatial mapping, and natural language processing, allowing AR systems to interact with the environment in a meaningful way. For example, AI-powered AR applications can identify objects in a user’s surroundings and provide real-time contextual information or assistance.
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks is a game-changer for AR. Faster internet speeds and lower latency enable real-time interactions and high-quality AR experiences without the need for bulky local processing power. This opens up possibilities for cloud-based AR solutions, where complex computations happen remotely while the user enjoys smooth, immersive interactions.
- Development Tools and Platforms: Advanced AR development platforms like ARKit, ARCore, and Vuforia make it easier for developers to create sophisticated AR applications. These tools provide pre-built features like motion tracking and 3D object detection, reducing development time and encouraging innovation.
AR in Entertainment and Gaming
The entertainment and gaming industries have been at the forefront of AR adoption, delivering some of the most immersive and interactive experiences to date. As technology evolves, AR is set to redefine how audiences consume and engage with media.
- Interactive Gaming
- Games like Pokémon GO showcased the potential of AR by blending virtual characters into real-world settings. Future AR games will likely build on this foundation, incorporating more complex interactions, multiplayer features, and adaptive storylines. AR gaming could also extend beyond mobile devices, with wearable AR devices offering a more intuitive and immersive experience.
- Live Performances and Events
- AR has the potential to enhance live concerts, theater performances, and sports events by adding dynamic, interactive layers. For example, AR could project virtual performers alongside real artists on stage or provide real-time player stats and replays during a sports game. These innovations could make live events more engaging and accessible to remote audiences.
- Immersive Storytelling
- AR offers unique opportunities for storytelling in movies and television. Viewers can step into augmented scenes, explore the environments, and interact with characters, creating a participatory experience that traditional media cannot achieve.
Revolutionizing Education and Training
One of the most promising applications of AR lies in its ability to transform learning and skill development. By making information visual, interactive, and contextual, AR enables more engaging and effective education and training experiences.
- Classroom Learning
- AR can bring textbooks and lessons to life, allowing students to explore complex concepts through visualizations. For instance, an AR app could display a 3D model of the solar system, enabling students to interact with planets, observe their orbits, and learn about their properties in real time.
- Corporate Training
- Companies are using AR to train employees in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and retail. Workers can practice tasks in a simulated environment before applying their skills in real-world scenarios. For example, AR can guide technicians through complex assembly processes step-by-step, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
- Remote Education
- AR enhances remote learning by creating virtual classrooms where students and teachers can interact as if they were physically present. This technology bridges the gap between in-person and online education, fostering a sense of connection and engagement.
AR in Retail and Marketing
AR is revolutionizing the retail and marketing industries by enhancing the shopping experience and offering innovative ways to engage customers.
- Virtual Try-Ons
- AR enables customers to try on products such as clothing, accessories, or makeup virtually. By using their smartphone or an AR-enabled device, shoppers can see how items will look on them before making a purchase, reducing returns and increasing confidence.
- Interactive Shopping Experiences
- AR can transform physical stores into interactive spaces. Customers can use their devices to scan products and access additional information, reviews, or promotional content. AR also allows retailers to create immersive displays and experiences that attract foot traffic.
- Targeted Advertising
- Marketers are using AR to create memorable advertising campaigns. For example, AR ads can overlay virtual elements onto real-world environments, enabling users to interact with a brand in innovative ways. This type of advertising not only grabs attention but also encourages active participation.
Transforming Healthcare with AR
AR is having a profound impact on healthcare by improving diagnosis, treatment, and patient education.
- Surgical Applications
- Surgeons are using AR to visualize internal anatomy during procedures, improving precision and reducing risks. AR overlays real-time data, such as MRI scans or vital signs, onto the patient’s body, helping surgeons make more informed decisions.
- Patient Education
- AR helps patients understand their medical conditions and treatments by visualizing complex medical information. For instance, an AR app could show a 3D model of a patient’s heart to explain a surgical procedure or the effects of a condition.
- Therapy and Rehabilitation
- AR is being used in physical therapy and mental health treatments. Patients can engage in AR-guided exercises or participate in virtual scenarios designed to treat phobias, PTSD, or anxiety.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
While the future of AR is promising, several challenges must be addressed for its full potential to be realized.
- Cost and Accessibility: High costs associated with AR devices and infrastructure remain a barrier to widespread adoption. Making AR technology affordable and accessible is crucial for its mainstream success.
- Privacy Concerns: AR applications often rely on collecting and analyzing user data, raising concerns about privacy and security. Establishing clear regulations and ethical guidelines will be essential to protect users.
- Technical Limitations: Current AR systems still face limitations in terms of battery life, processing power, and environmental recognition. Ongoing advancements in hardware and software are needed to overcome these issues.
 (Image source: Midjourney)
(Image source: Midjourney)