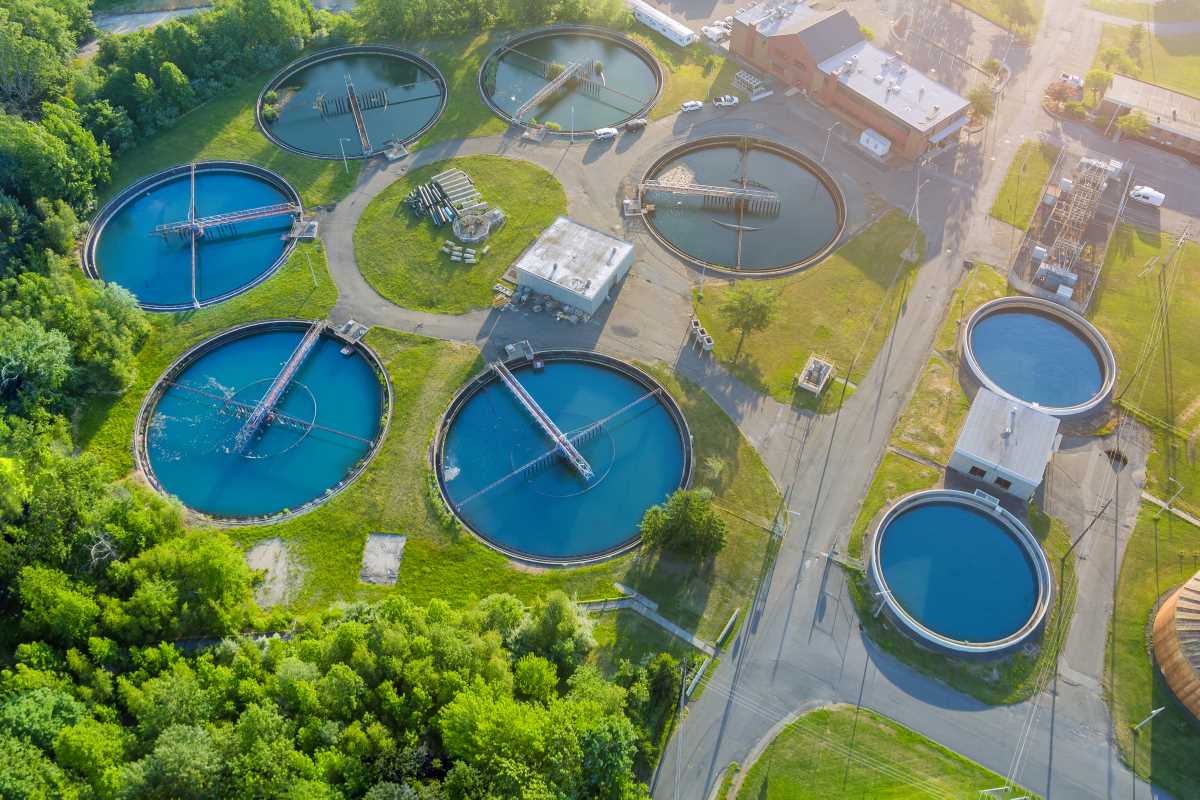
Access to clean water is a fundamental human right and a critical component of a sustainable future. However, with growing populations, industrialization, and climate change, water resources are becoming increasingly stressed. Water pollution, over-extraction, and climate-induced droughts are all exacerbating the global water crisis. To address these challenges, pioneering water purification technologies are emerging as key solutions for providing clean, safe drinking water and ensuring water sustainability for future generations. These innovations range from advanced filtration techniques to decentralized water treatment systems, all playing a crucial role in alleviating water scarcity and contamination problems worldwide.
The Need for Advanced Water Purification
The United Nations reports that 2.2 billion people around the world lack access to safely managed drinking water, with water quality issues often tied to contamination from pollutants like bacteria, heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial waste. In addition to contamination, the global demand for water is rapidly increasing, with the World Health Organization (WHO) estimating that by 2025, two-thirds of the world’s population could be living in water-stressed regions.
Traditional water purification methods, such as boiling or chlorination, are effective in certain contexts, but they are often inadequate in dealing with more complex pollutants or large-scale water demands. This has created a need for new, innovative water purification technologies that can address both present challenges and future demands for clean water.
Cutting-Edge Water Purification Technologies
1. Reverse Osmosis (RO)
One of the most widely adopted water purification methods is reverse osmosis (RO), which uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove dissolved salts, chemicals, and pathogens from water. By applying pressure, water is pushed through the membrane, leaving contaminants behind. This process is highly effective in desalinating seawater and purifying brackish water, making it potable.
Advancements in RO technology have led to more energy-efficient systems, reducing the energy consumption that was once a limitation of the process. Innovations such as graphene-based membranes, which are more efficient and durable than traditional materials, are set to revolutionize RO technology, making it more affordable and accessible to a wider population.
2. Solar-Powered Water Purification
With over 1.3 billion people lacking access to electricity, solar-powered water purification systems offer a promising, low-cost solution. These systems use solar energy to power water purification processes, including distillation, filtration, and UV sterilization. Solar stills, for example, harness solar heat to evaporate water, leaving contaminants behind, and then condense the vapor into pure water. Solar-powered desalination systems are another promising development. These systems use solar energy to heat seawater, converting it into vapor and condensing it into freshwater. Solar desalination not only provides an eco-friendly solution for water purification but also holds promise for off-grid communities in remote, water-scarce areas.
3. Graphene Filters
Graphene, a two-dimensional material made of a single layer of carbon atoms, has recently garnered significant attention for its potential to revolutionize water filtration. Graphene oxide membranes are highly effective at filtering out nanoparticles, salts, and even organic pollutants. What makes graphene so promising is its ability to filter water at a molecular level, enabling ultra-efficient purification processes.
Researchers have been exploring the potential of graphene-based filtration systems to desalinate seawater and remove heavy metals, pathogens, and toxins from contaminated water. The technology promises a more energy-efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable approach to water purification, with the potential to address global water scarcity issues.
4. Bio-inspired Filtration
Nature has perfected the art of filtration over billions of years, and scientists are increasingly turning to nature’s designs for inspiration. Bio-inspired filtration technologies mimic the natural filtering mechanisms found in organisms like plants, fish, and even bacteria. One example is the development of bio-sand filters, which use layers of sand, gravel, and biological materials to filter out impurities in water.
Researchers are also investigating bio-inspired nanomaterials that mimic the structure of certain plant membranes, which allow water to pass through while blocking contaminants. These bio-inspired solutions have the potential to provide highly efficient and sustainable filtration processes, especially for rural or underserved areas where access to advanced technology is limited.
5. Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is a relatively new water treatment method that uses electrical currents to remove contaminants from water. The process involves applying a direct current to water, which causes dissolved contaminants, such as heavy metals, oils, and bacteria, to coagulate and form larger particles that can be easily removed by filtration.
This method has several advantages, including its ability to treat a wide range of contaminants, its relatively low energy consumption, and its ability to operate without the need for chemical additives. Electrocoagulation systems are becoming increasingly popular for industrial wastewater treatment, but they also hold promise for treating drinking water in areas affected by pollution.
6. Ozonation
Ozone (O₃) is a powerful oxidant that has been used for decades in water treatment to disinfect and remove harmful microorganisms. Ozonation systems introduce ozone gas into water, where it breaks down pollutants, including organic compounds, bacteria, and viruses. The ozone is then converted back to oxygen, leaving no harmful residues behind.
Recent developments in ozonation technology have improved its efficiency and reduced its cost, making it a more viable option for large-scale water purification projects. Ozone treatment also offers the advantage of being able to purify water without the use of chemicals like chlorine, making it an environmentally friendly option for water disinfection.